Content
- FASB removes goodwill project from its technical agenda
- What is the difference between depreciation and amortization?
- How to Fix End of Year Balance Sheet With Overstated Assets
- Example Question #1 : Depreciation And Amortization
- What Pertinent Items Can You Write Off on Taxes?
- Amortization vs. Depreciation: An Overview
- AMORTIZATION

The periods over which intangible assets are amortized vary widely, from a few years to 40 years. Leasehold interests with remaining lives of three years, for example, would be amortized over the following three years. The costs incurred with establishing and protecting patent rights would generally be amortized over 17 years. The goodwill recorded in connection with an acquisition of a subsidiary could be amortized Amortization Accounting over as long as 40 years past the author’s death, and should also be limited to 40 years under accounting rules. The general rule is that the asset should be amortized over its useful life. When a business purchases intangible assets, it must report the purchase on its balance sheet. However, businesses often spread the cost of larger purchases over several years in a process known as amortization.
- In business, accountants define amortization as a process that systematically reduces the value of an intangible asset over its useful life.
- You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in oureditorial policy.
- The goodwill recorded in connection with an acquisition of a subsidiary could be amortized over as long as 40 years past the author’s death, and should also be limited to 40 years under accounting rules.
- Then subtract the interest from the payment value to get the principal.
- We record the amortization of intangible assets in the financial statements of a company as an expense.
The staff has prepared this summary for information purposes only. Any Board decisions are tentative and do not change current accounting.
FASB removes goodwill project from its technical agenda
A mortgage recast takes the remaining principal and interest payments of a mortgage and recalculates them based on a new amortization schedule. For the next month, the outstanding loan balance is calculated as the previous month’s outstanding balance minus the most recent principal payment. On December 31, year 1, the company will have to pay the bondholders $5,000 (0.05 × $100,000). The cash interest payment is the amount of interest the company must pay the bondholder. The company promised 5% when the market rate was 4% so it received more money. But the company is only paying interest on $100,000—not on the full amount received. The difference in the sale price was a result of the difference in the interest rates so both rates are used to compute the true interest expense.

If an intangible asset has an indefinite lifespan, it cannot be amortized (e.g., goodwill). Loan amortization, a separate concept used in both the business and consumer worlds, refers to how loan repayments are divided between interest charges and reducing outstanding principal. Amortization schedules determine how each payment is split based on factors such as the loan balance, interest rate and payment schedules. The debit balances in some of the intangible asset accounts will be amortized to expense over the estimated life of the intangible asset. Fixed/tangible assets are purchased and used, they decrease in value over time.
What is the difference between depreciation and amortization?
If the repayment model on a loan is not fully amortized, then the last payment due may be a large balloon payment of all remaining principal and interest. If the borrower lacks the funds or assets to immediately make that payment, or adequate credit to refinance the balance into a new loan, the borrower may end up in default. The difference between amortization and depreciation is that depreciation is used on tangible assets. Tangible assets are physical items that can be seen and touched. For example, vehicles, buildings, and equipment are tangible assets that you can depreciate.
How do you calculate amortization of intangible assets?
The company should subtract the residual value from the recorded cost, and then divide that difference by the useful life of the asset. Each year, that value will be netted from the recorded cost on the balance sheet in an account called "accumulated amortization," reducing the value of the asset each year.
This document/information does not constitute, and should not be considered a substitute for, legal or financial advice. Each financial situation is different, the advice provided is intended to be general. Please contact your financial or legal advisors for information specific to your situation.
How to Fix End of Year Balance Sheet With Overstated Assets
For tax purposes, amortization can result in significant differences between a company’s book income and its taxable income. For intangible assets, companies use the asset’s useful life to divide its cost over time, while for loans, they use to number of periods for payments. Record amortization expenses on the income statement under a line item called “depreciation and amortization.” Debit the amortization expense to increase the asset account and reduce revenue. Valuing intangible assets that were developed by your company is much more complex, because only certain expenses can be included. Only the costs to secure the patent, such as legal, registration and defense fees, can be amortized. The costs incurred to develop the technology, such as R&D facilities and your engineers’ salaries, are deductible as business expenses. For this article, we’re focusing on amortization as it relates to accounting and expense management in business.

Residual value is the estimated value of a fixed asset at the end of its lease term or useful life. With depreciation, amortization, https://www.bookstime.com/ and depletion all are non-cash expenses. That is, no cash is spent in the years for which they are expensed.
Example Question #1 : Depreciation And Amortization
You should record $1,000 each year in your books as an amortization expense. Entrepreneurs often incur startup costs to organize a business before it begins operating.
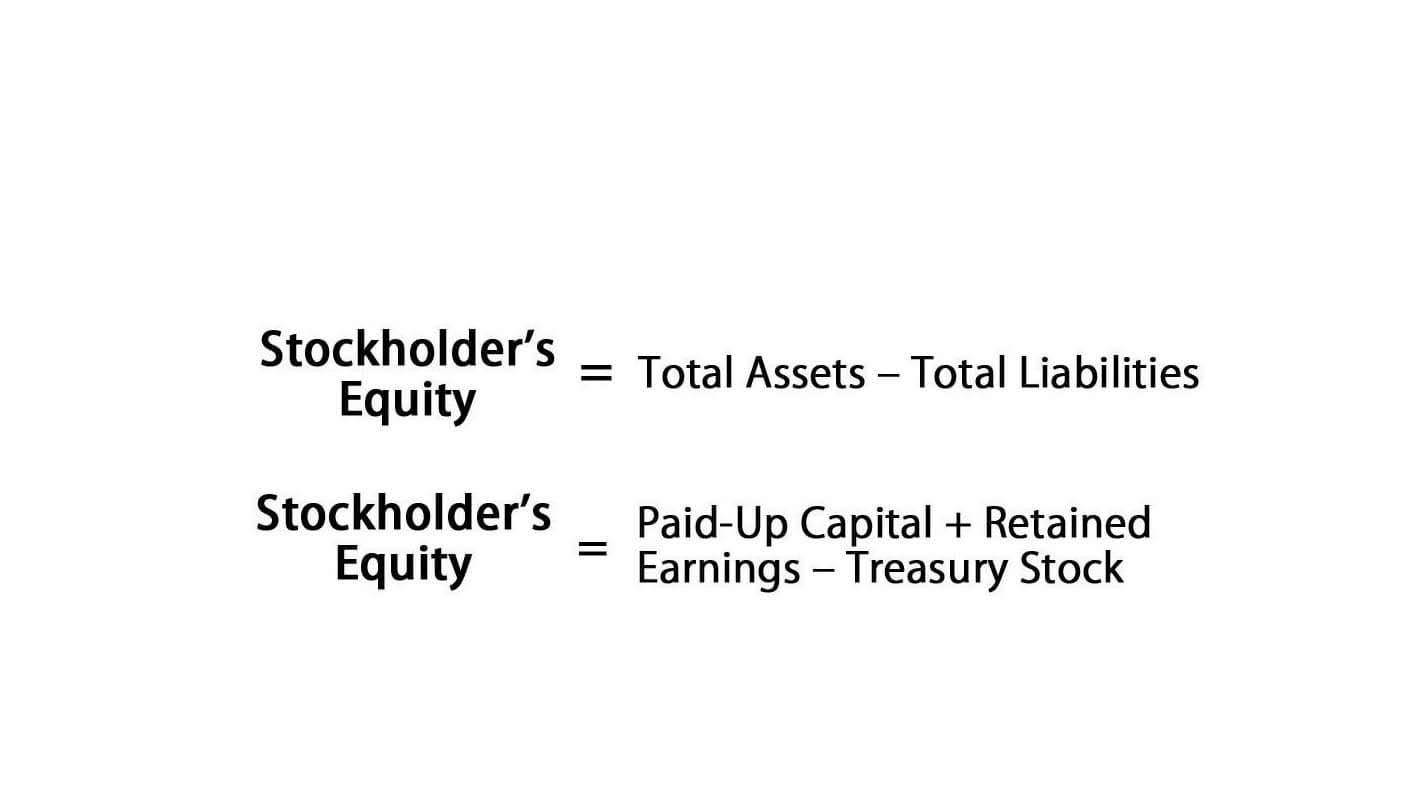
Similar todepreciationof tangible assets, intangible assets are typically expensed over the course of the asset’s useful life. It represents reduction in value of the intangible asset due to usage or obsolescence. Basically, intangible assets decrease in value over time, and amortization is the method of accounting for that decrease in value over the course of the asset’s useful life. A company’s long-termcapital expenditures can also be amortized over time. For example, a company benefits from the use of a long-term asset over a number of years.